OBP-702
- Outline / Target indication
- Mechanism
The Target: Telomerase – essential to cancer cell immortalization

Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds TTAGGG telomere repeats onto the 3’ends of telomeres of each chromosome, to protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from chromosome fusion. Telomerase is crucial for the survival of cancer cells.

The majority (>80%) of malignant tumors express telomerase activity, whereas telomerase is strongly repressed in most normal somatic tissues. Telomerase may be a promising target for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
The Target 2: a tumor suppressor p53 – essential to cancer cell immortalization
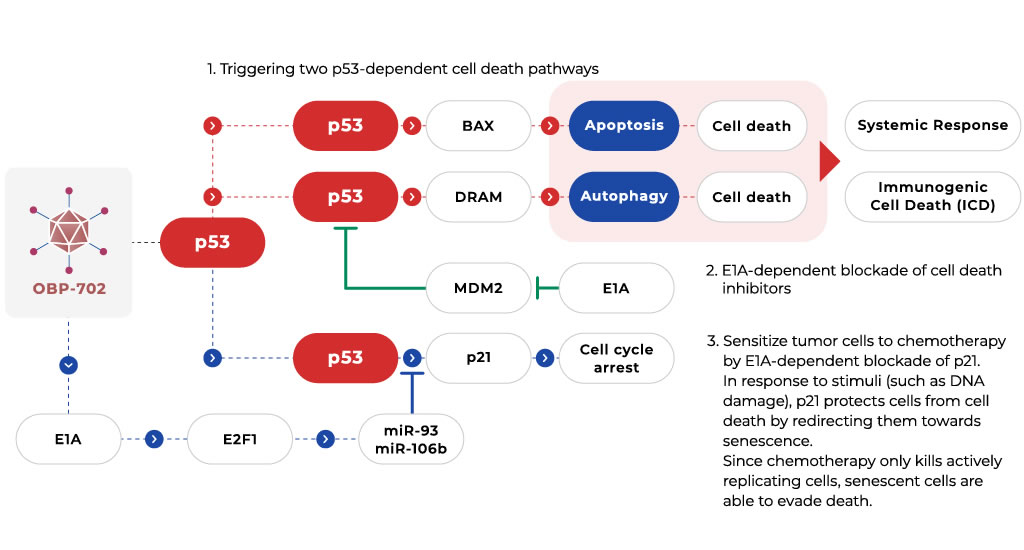
Proposed Immune-Priming Activity of OBP Oncolytic Virus: Turning the Cold Tumors HOT for Immunotherapies

Radiotherapy
Telomelysin (OBP-301), the first generation of OBP-702, increases radiosensitization by blocking DNA repair
In mouse models of human cancer, TelomelysinTM induced a synergistic antitumor effect due to tumor cell-specific radiosensitization when combined with regional irradiation.Checkpoint inhibition
Telomelysin (OBP-301) may synergize with anti-PD-1 antibodies by increasing tumor immunogenicity
In preclinical murine models, Telomelysin™ induced immunogenic cell death, sensitizing non-immunogenic gastrointestinal tumors to PD-1 Ab.